Stack
A stack is an ordered collection of items into which
new items may be inserted and from which item may be deleted at one end called
top of the stack.
The operation
of inserting the item in a stack is called PUSH.
The
operation of removing the item from the stack is called POP.
Algorithm for PUSH operation
1. Check
if stack is full or not
i.e. if (TOP = maxsize – 1)
then print stack is full or stack
overflow
2. Increase
the value of TOP by one
TOP = TOP + 1
3. Insert
the element at the TOP of the stack
i.e. Stack[TOP] = data
4. Exit
Algorithm for PUSH operation
1. Check
if stack is empty or not
i.e. if (TOP == - 1)
then print pop operation cannot be
performed
2. Remove
the data from the stack
3. Decrease
the value of TOP by one
i.e. TOP = TOP -1
4. Exit
Program to perform various operation in Stack (Implemented in C programming)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<process.h>
#define maxsize 20
int stack[maxsize],TOS=-1;
void display()
{
int j;
for(j=TOS;j>=0;j--)
{
printf("\nThe number is
%d\n",stack[j]);
}
}
void push()
{
int y;
if(TOS==maxsize-1)
{
printf("Stack overflow\n");
}
else
TOS=TOS+1;
printf("Enter new element\n");
scanf("%d",&y);
stack[TOS]=y;
printf("%d is
inserted\n",stack[TOS]);
display();
}
void pop()
{
if(TOS==-1)
printf("Stack overflow");
else
printf("The element is
%d\n",stack[TOS]);
TOS=TOS-1;
display();
}
void main()
{
int stack[maxsize],i;
char ch;
while(1)
{
printf("Enter 1 for push 2 for pop
and 3 for DISPLAy\n");
scanf("%d",&i);
switch(i)
{
case 1:
printf("PUSH\n");
push();
break;
case 2:
printf("POP\n");
pop();
break;
case 3:
printf("DISPLAY\n");
display();
break;
default:
printf("Error occurs");
}
}
}
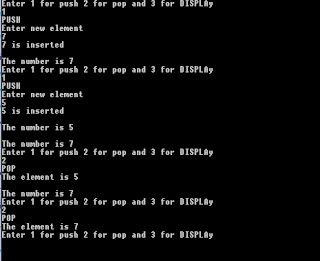
Sample Output:
Implemented in C++ programming
#include<iostream>
#define size 5
using namespace std;
class stack
{
private :
int
top;
int
itm[size];
public :
stack()
{
top=-1;
}
int
empty()
{
if
(top==-1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void
pop()
{
if(empty()==true)
cout<<"\nStack underflow\n";
else
{
cout<<"Element "<<itm[top]<<"Popped
out.\n";
top--;
}
}
void
push(int i)
{
if(top>size-1)
cout<<"\nStack Overflow\n";
else
{
itm[++top]=i;
cout<<"Element
"<<itm[top]<<"pushed.\n";
}
}
int
tp()
{
return itm[top];
}
};
int main()
{
stack s;
s.push(6);
s.push(5);
s.push(4);
s.push(3);
s.push(2);
s.push(1);
s.push(0);
s.tp();
cout<<"\n";
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}
No comments:
Post a Comment